Renowned for its unique qualities, Aspen wood presents a compelling array of advantages and drawbacks worth exploring.

- Overview of aspen wood
- Aspen wood pros
- Aspen wood is lightweight and easy to work with
- Aspen wood is aesthetically pleasing
- Aspen wood is versatile in finishing
- Aspen wood is environmentally sustainable
- Cons of using aspen wood
- Aspen wood is soft and prone to denting
- Aspen wood is susceptible to damage and decay
- Aspen wood has limited structural applications
- Maintenance and care tips for aspen wood
- Conclusion
- FAQ
- What are the cons of aspen wood?
- What is aspen wood good for?
- Why not to plant aspens?
- Is aspen good for outdoor use?
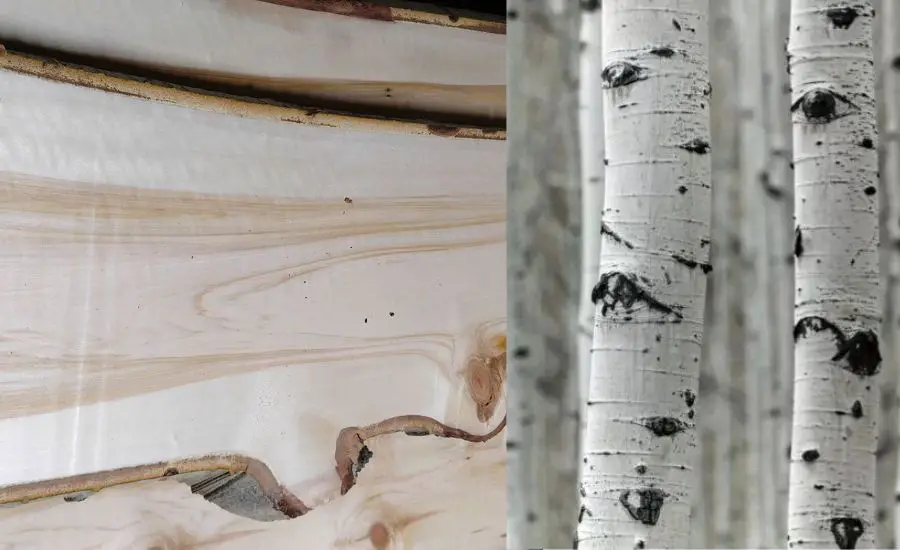
Overview of aspen wood
Quacking/trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides), derived from the deciduous tree, is a popular and versatile soft hardwood species primarily found in eastern North America – bigtooth aspen (but there are other varieties like Korean aspen, Chinese aspen, Japanese aspen, and Eurasian/European aspen).
Recognized for its light color, medium texture, and porous structure, aspen wood is often sought after for various woodworking projects and applications.
- Aspen wood for furniture making
Lightweight furniture: using aspen wood is an excellent choice for crafting furniture, especially where portability or ease of movement is essential, such as chairs, stools, and tables.
Decorative pieces: using aspen wood is a common practice for crafting decorative furniture items like cabinets, shelves, and ornamental pieces due to its aesthetic appeal and workability, allowing intricate designs.
Indoor and limited outdoor use: using aspen wood in indoor furniture is the most common choice. However, with proper treatment, it can be suitable for covered outdoor projects.
- Aspen wood in construction
Non-structural components: this soft hardwood is used in non-structural elements of construction, such as trim work, interior paneling, and molding due to its workability and pleasing appearance.
Crafting small structures: using aspen wood is suitable for crafting smaller structures like sheds, playhouses, or gazebos where load-bearing requirements are not demanding.
- Craft and artistic applications of aspen wood
Woodworking crafts: aspen wood is popular among woodworkers for crafting various items like carvings, turnings, and scrollwork due to its ease of manipulation.
Artistic and sculptural works: artists appreciate aspen wood for sculpting and artistic projects, using its softer nature for detailed carving and intricate woodworking projects.
Woodturning and lathe work: aspen’s workability on a lathe makes it ideal for producing turned items such as bowls, vases, and decorative pieces.
However, while aspen wood holds several advantageous characteristics, it’s essential to delve into its pros and cons to gain a comprehensive understanding of its suitability for different applications.

Aspen wood pros
Exploring the numerous advantages of aspen woods reveals its appeal due to unique characteristics that offer a blend of lightweight manageability and versatile applications in woodworking.
Aspen wood is lightweight and easy to work with
Exceptional lightweight quality: this soft hardwood stands out due to its remarkably lightweight nature compared to some other woods like Brazilian cherry, facilitating easy handling and manipulation during woodworking tasks.
This characteristic reduces physical strain on craftsmen and enhances precision in intricate designs.
Ease of workability: one of the aspen wood properties is its low density which contributes to its ease of workability, allowing for effortless cutting, shaping, and carving with power tools.
This quality of aspen wood makes it a preferred material for artisans seeking responsiveness to various woodworking tools.
Appeal to hobbyists and professionals: its combination of manageability and reasonable structural integrity attracts both professionals and hobbyists looking for a wood type that balances ease of use with durability in various projects, like other hardwoods.
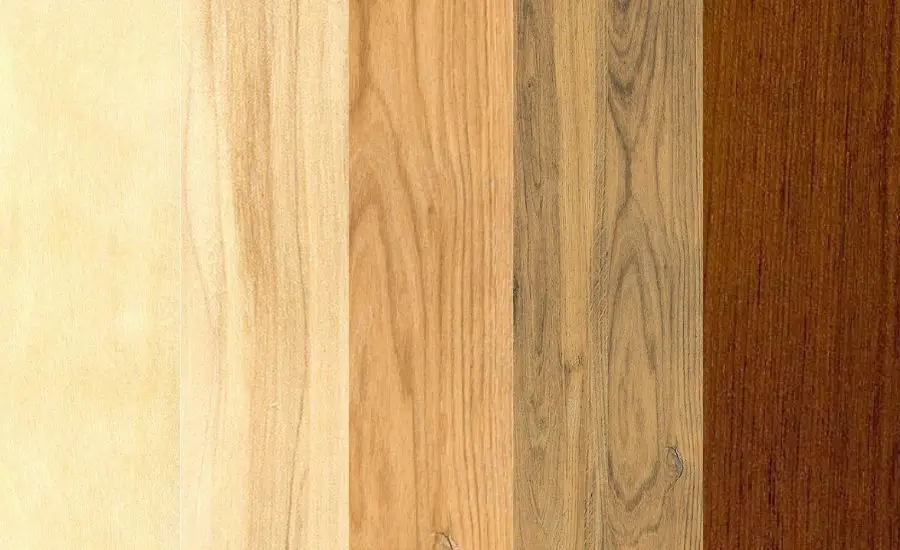
Aspen wood is aesthetically pleasing
Pale to light brown hue: the aspen tree exhibits a naturally appealing color palette, ranging from pale white to light brown.
Subtle and attractive grain patterns: the straight grain patterns found in the aspen tree contribute to its visual allure. While generally fine, these straight-grain patterns occasionally feature subtle knots and unique swirls, adding character and visual interest to finished pieces.

Aspen wood is versatile in finishing
Excellent absorption of finishes: aspen wood is highly porous, allowing it to readily absorb various finishes such as stains, paints, and varnishes.
Customizable appearance: its ability to absorb finishes effectively offers woodworkers the opportunity to achieve a wide spectrum of looks and styles.
From natural and clear varnishes highlighting the wood’s natural beauty to vibrant paints or darker stains, aspen wood can be customized to suit diverse design preferences.
Enhanced protection: finishing treatments not only augment the aesthetic appeal but also provide protective layers. This added protection prolongs the lifespan of aspen wood.
Aspen wood is environmentally sustainable
Rapid growth rate: aspen trees are known for their rapid growth, making them a highly renewable resource in the forestry industry.
Aspen trees reproduce quickly, allowing for sustainable harvesting practices without significantly depleting forests.
Minimal environmental impact: the harvesting of aspen trees is relatively eco-friendly due to its regenerative nature. Responsible forestry practices focus on selective cutting and replanting, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of aspen trees.
Carbon sequestration: aspen trees contribute to carbon sequestration by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass.
Versatile applications in green building: quaking aspen trees provide sustainability that aligns with the principles of green building.
Using aspen trees in eco-friendly construction practices and the creation of renewable wood products supports environmentally conscious building initiatives.

Cons of using aspen wood
When considering the use of aspen wood, several drawbacks merit attention, presenting potential challenges in various applications.
Aspen wood is soft and prone to denting
Softness and susceptibility to dents: this soft wood, while offering advantages in workability, presents notable vulnerabilities in terms of durability.
Its relatively soft composition renders it more prone to dents, scratches, and surface damage similar to some other hardwoods like poplar wood.
This soft hardwood has a wood species hardness value of 420 lbf (1,868 N) on the Janka hardness scale, which is lower than the hardness rating of most hardwoods.
The soft nature of aspen wood, while advantageous for certain woodworking processes that require ease of manipulation, becomes a concern when it comes to sustaining the appearance and structural integrity of this not-so-durable wood over time.

Aspen wood is susceptible to damage and decay
Moisture sensitivity: aspen wood’s lower density makes it more susceptible to moisture absorption than other hardwoods.
Vulnerability to rot: the increased moisture absorption can contribute to rotting or decay in aspen wood if proper precautions and maintenance aren’t implemented.
Risk of mold and mildew: moist conditions can foster the growth of mold and mildew on aspen wood surfaces, affecting its aesthetic appeal and potentially causing health concerns if not addressed promptly and adequately.
Limited resistance to insects: aspen’s porous nature and susceptibility to moisture make it an inviting target for insects.
Aspen wood has limited structural applications
Lower load-bearing capacity: quaking aspen wood’s relatively lower density and strength compared to some hardwoods limit its suitability for heavy load-bearing applications.
Restricted use in intensive structural elements: in applications demanding high strength, such as load-bearing beams or structural frameworks, aspen’s limitations in strength may render it unsuitable.
Consideration for weight-bearing structures: due to its lightweight nature, aspen wood is more appropriate for lightweight constructions where its structural limitations are less critical.
Replacement with harder woods: in scenarios necessitating robustness and superior load-bearing capabilities, builders and engineers often opt for harder woods like oak or maple, which provide enhanced structural support and durability compared to aspen wood.
Maintenance and care tips for aspen wood
Implementing effective maintenance and care practices is crucial to preserve the longevity and visual appeal of aspen wood.
- Proper treatment and finishing of aspen wood
Sealing and finishing: apply suitable sealants, varnishes, or finishes to aspen wood surfaces to protect against moisture absorption, scratches, and other forms of damage.
Regular cleaning: periodically clean aspen wood using a mild solution of soap and water, ensuring thorough drying afterward to prevent moisture retention.
Avoiding direct sunlight and extreme conditions: minimize prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations as they can cause aspen wood to warp or fade.
Routine inspections: regularly inspect aspen wood furniture or structures for signs of damage, such as dents, scratches, or moisture-related issues. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
Reapplication of finishes: over time, reapply finishes or protective coatings as needed, following manufacturer recommendations. This helps maintain the protective layer of aspen wood, ensuring prolonged durability and aesthetic appeal.

- Preventative measures to preserve aspen wood
Controlled environmental conditions: maintain consistent humidity levels and temperature in the surroundings to prevent excessive moisture absorption or extreme fluctuations that could adversely affect the aspen wood.
Use dehumidifiers or humidifiers as needed to maintain optimal conditions.
Use of protective coatings: apply protective coatings such as polyurethane, lacquer, or sealants specifically designed for wood surfaces.
These coatings act as barriers, shielding aspen wood from moisture, scratches, and UV damage, thereby prolonging its lifespan.
Avoiding direct ground contact: elevate aspen wood structures or furniture above ground level to prevent direct contact with moisture-prone surfaces.
This precaution helps mitigate the risk of moisture absorption and potential decay from contact with damp ground.
Regular inspections and maintenance: conduct routine checks for signs of damage, such as cracks, water stains, or insect infestations. Promptly address any issues through repairs or treatments to prevent further deterioration.
Proper storage and handling: store aspen wood products in dry, well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and moisture sources. When handling, use appropriate techniques and protective padding to prevent accidental damage.

Conclusion
In weighing the pros and cons of aspen wood, it emerges as a versatile material with unique characteristics, requiring thoughtful consideration and proper maintenance to maximize its benefits in various applications.
FAQ
What are the cons of aspen wood?
Susceptibility to denting, moisture-related damage, and limited structural strength, unlike other hardwoods.
What is aspen wood good for?
European aspen, bigtooth aspen, and its other varieties are ideal for lightweight furniture making, decorative pieces, non-structural construction, woodworking crafts, and artistic projects due to their workability and aesthetic appeal.
For example, aspen hardwood flooring pros include light and elegant appearance, easy workability, customizable finishes, and environmental sustainability.
Why not to plant aspens?
Aspens can spread aggressively through their root systems, potentially causing issues with overcrowding and maintenance.
Is aspen good for outdoor use?
Aspen wood is generally not recommended for direct outdoor exposure due to its vulnerability to moisture unless adequately treated and protected against decay and weathering.


![Sapele vs. walnut wood [5 main differences] Sapele Vs. Walnut Wood: Top 5 Differences & Best Guide](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/wood-53-335x220.jpg)
![Mango wood furniture pros and cons [9 tips] Mango wood furniture pros and cons + 9 tips before you buy](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/wood-51-335x220.jpg)

![Which advantages and disadvantages of hickory wood? [8 factors] Top 8 Disadvantages Of Hickory Wood: Best Helpful Guide](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/wood-38-335x220.jpg)

![How Long Do Wood Pellets Last? [6 Essential Insights Unveiled] How long do wood pellets last](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/How-Long-Do-Wood-Pellets-Last-6-Essential-Insights-Unveiled-2-335x220.jpg)
![Tung oil vs polyurethane [4 main comparison factors] Tung Oil Vs Polyurethane: Top 4 Factors & Best Helpful Guide](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/wood-14-335x220.jpg)
![Is tung oil flammable? [7 Preventive measures] Is Tung Oil Flammable: Top 7 Safe Tips & Best Guide](https://bestwoodforcarving.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/What-is-a-Wood-Planer-3-335x220.jpg)
